A/B Testing
Run experiments to find the best performing landing page variants and optimize your conversion rates.
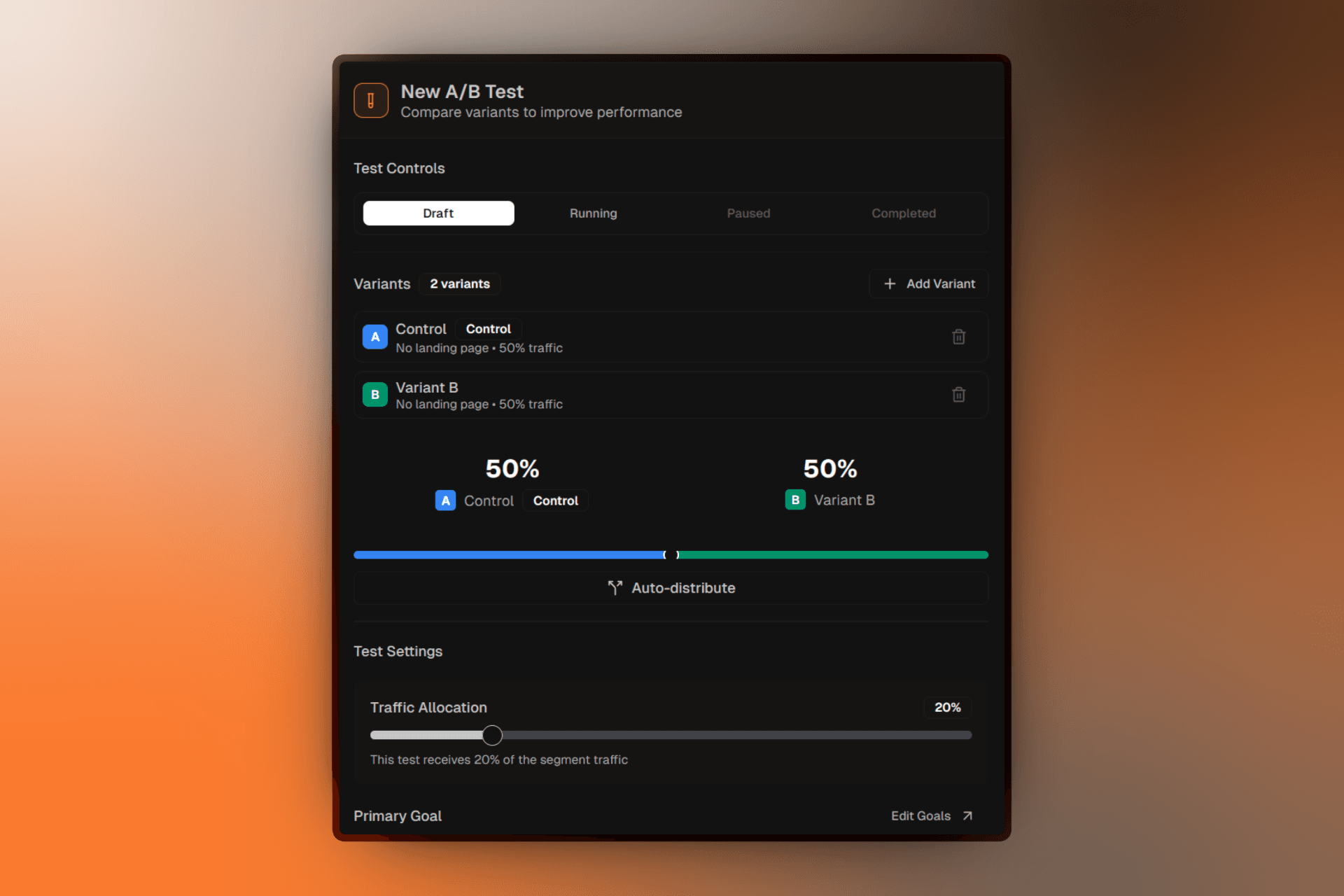
A/B testing lets you compare different versions of your landing pages to see which one performs best. Firebuzz handles traffic distribution, data collection, and statistical analysis automatically.
What Is A/B Testing?
A/B testing (also called split testing) is a method of comparing two or more versions of a landing page to determine which one performs better for a specific goal.
Compare Variants
Test up to 5 different landing page versions simultaneously.
Automatic Traffic Split
Traffic is automatically distributed between variants based on your settings.
Statistical Confidence
Get statistically significant results with configurable confidence levels.
Clear Winners
The system identifies which variant performs best for your primary goal.
How A/B Tests Work
- Create an A/B Test within a segment
- Add Variants with different landing pages (2-5 variants)
- Start the Test when your campaign is published
- Traffic is Split between variants automatically
- Data is Collected on conversions and engagement
- Winner is Determined based on statistical significance
A/B Test Lifecycle
Every A/B test goes through these statuses:
Draft
Test is being configured. No traffic is being split yet.
Running
Test is active, collecting data, and splitting traffic.
Paused
Test is temporarily stopped. Traffic goes to primary landing page.
Completed
Test has finished. Winner has been determined.
Status Transitions
Draft → Running (when started)
Running → Paused (when paused)
Paused → Running (when resumed)
Running/Paused → Completed (when marked complete)Only one A/B test per segment can be in Draft, Running, or Paused status at a time. You can have multiple Completed tests for historical reference.
Creating A/B Tests
Step-by-step guide to setting up your first experiment.
Managing Variants
Learn how to add, configure, and manage test variants.
Key Concepts
Control Variant
The control is your baseline — typically your current or original landing page. All other variants are compared against it.
- One variant must always be marked as control
- The control variant cannot be deleted
- You can change which variant is the control
Traffic Distribution
Traffic is split between variants based on percentages you configure:
| Variant | Traffic % |
|---|---|
| Control | 50% |
| Variant B | 50% |
With more variants, traffic is split automatically:
| Variant | Traffic % |
|---|---|
| Control | 34% |
| Variant B | 33% |
| Variant C | 33% |
Pooling Percentage
The pooling percentage determines how much of the segment's traffic enters the A/B test vs. going directly to a default experience.
- 20% (default): 20% of segment traffic goes to the A/B test
- 100%: All segment traffic goes to the A/B test
Start with a lower pooling percentage to limit exposure while testing risky changes.
Completion Criteria
Define when your test has collected enough data:
- Sample Size: Number of conversions per variant (e.g., 1,000 per variant)
- Duration: How long the test runs (e.g., 14 days)
Confidence Level
The statistical confidence required to declare a winner (default: 95%).
Higher confidence = more certainty but requires more data.
FAQ
Troubleshooting
For common A/B testing issues, see A/B Test Troubleshooting.